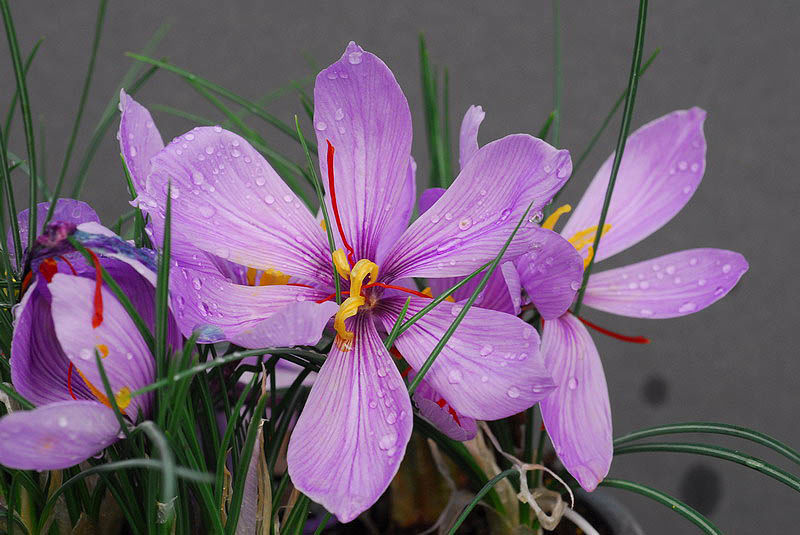

Crocus sativus, or saffron crocus, is a flowering plant in the iris family. Also it blooms in autumn. And produces floral stigmas. People use these stigmas to make saffron, a spice. In fact Saffron cultivation and trade have lasted over 3,500 years. Similarly various cultures and continents have used it.
Crocus Sativus Names
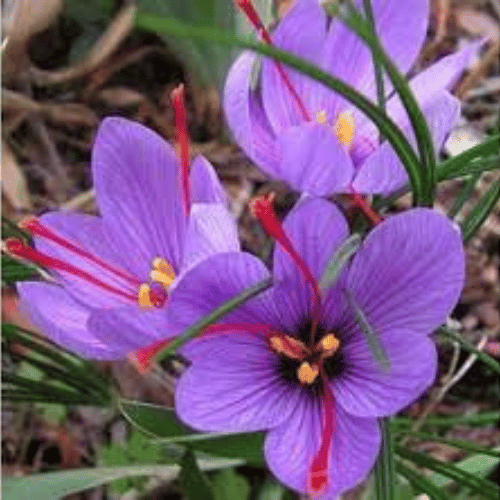

Also people often call the plant saffron crocus. The name autumn crocus also refers to Colchicum species. Moreover Colchicum plants are not closely related to true crocuses. Sometimes it also call Colchicum autumnale meadow saffron. True crocuses have three stamens. And one style with three stigmas. Colchicums have six stamens and three styles. It belong to the Colchicaceae family. Colchicums are toxic, unlike saffron crocus.
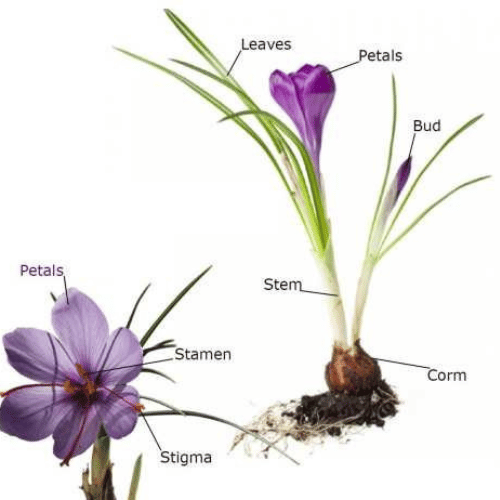
Crocus sativus is a perennial herb growing 10 to 30 cm high. Also it grows from an underground corm. Crocus sativus produces leaves, bracts, bracteoles, and a flowering stalk. It blooms with purple flowers in autumn. The flowers have six petals and three red-orange stigmas. But the leaves are simple and rosulate with entire margins.
Uses
The flower’s stigmas are used as the spice saffron. Also used in traditional Asian medicine. It contains active compounds like alkaloids. Saffron can enhance mood. Even in people with major depressive disorder. Harvesting 1 pound of saffron requires 50,000 to 75,000 flowers. Each corm produces one or two flowers. Each flower has three stigmas. Stigmas are harvested mid-morning when flowers are open. Saffron crocus can also be an ornamental plant.
Cultivation : Crocus sativus is sterile. And needs manual propagation. All plants are clonal with minimal genetic diversity. Desirable traits are hard to breed due to this. Cultivars are produced by:
- Clonal selection keeps plants with good mutations.
- Mutation breeding causes mutations for selection.
- Sexual reproduction is easier in fertile plants.
Saffron can cross-pollinate with wild relatives in vitro. Then this forms fertile diploid plants with new traits. Chromosome doubling can create a fertile hexaploid plant. Colchicine may help in this process. Plant corms 10 cm apart and 10 cm deep. The flower needs full sun and well-drained soil. Corms multiply yearly and last 3–5 years.
Daily Article: Darlingtonia californica
Watch Now : Drama Updates



